EQ-i 2.0 Emotional Intelligence Assessment
Recognized by Forbes and and validated by over 20 years of scientific research: The premier assessment for developing leaders who lead with authentic impact, empower high-performing teams and consistently deliver exceptional business results
Understanding Emotional Intelligence
Emotional intelligence is the ability to recognize, understand, and effectively manage emotions—both your own and those of others. It encompasses a set of emotional and social skills that influence how we perceive ourselves, express our thoughts and feelings, develop relationships, cope with challenges, and use emotional information to make effective decisions.
At AdvantEdge Leadership, we view emotional intelligence as the foundation for navigating strategic discomfort and driving organizational transformation. Leaders with advanced emotional intelligence create environments where innovation thrives, efficiency improves, and transformational change succeeds.
Why Emotional Intelligence Matters in the Workplace?
In today's complex business environment, emotional intelligence has emerged as a critical differentiator of high-performing organizations. Research consistently demonstrates its profound impact:
ORGANIZATIONAL PERFORMANCE
- 90% of top performers score high in emotional intelligence, while only 20% of bottom performers do (Harvard Business Review)
- Organizations with emotionally intelligent leadership outperform yearly earnings goals by 20% (Hay/McBer Research)
- Companies that prioritize EI development see up to 63% lower employee turnover (Center for Creative Leadership)
TEAM EFFECTIVENESS
- Teams led by emotionally intelligent managers experience 27% higher engagement levels (Gallup)
- Cross-functional collaboration improves by 35% when teams score high in collective emotional intelligence (Consortium for Research on Emotional Intelligence)
- Innovation cycles accelerate by 33% in environments where emotional intelligence is prioritized (McKinsey)
INDIVIDUAL IMPACT
- Decision quality improves by 42% when leaders apply emotional intelligence competencies (Journal of Organizational Behavior)
- Stress resilience increases by 68% for professionals with high emotional intelligence (American Psychological Association)
- Conflict resolution effectiveness improves by 58% with advanced emotional intelligence skills (Center for Creative Leadership)
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE IN LEADERSHIP: THE CRITICAL ADVANTAGE
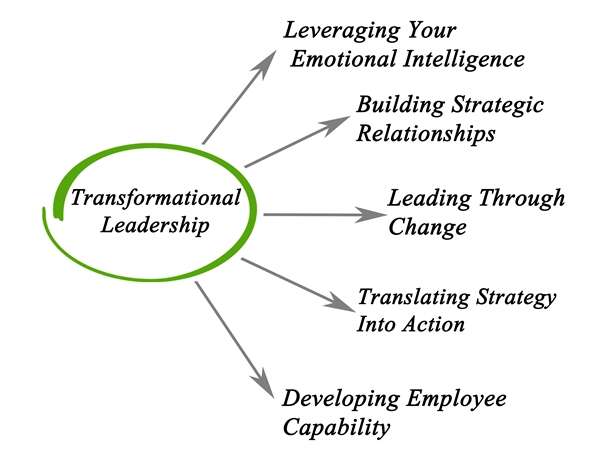
The most effective leaders in today's business environment distinguish themselves not just through technical expertise or strategic acumen, but through their mastery of emotional intelligence. This distinction becomes increasingly critical as leaders advance to more senior positions where influencing others, making complex decisions under pressure, and navigating organizational change become paramount.
TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP
Emotionally intelligent leaders create environments where transformation thrives. They:
- Navigate resistance to change by recognizing and addressing emotional barriers
- Maintain team cohesion during periods of strategic discomfort and uncertainty
- Inspire commitment to a shared vision through authentic connection
- Calibrate the right amount of productive tension to drive innovation without triggering disengagement
DECISION-MAKING UNDER PRESSURE
When stakes are high and tensions rise, emotionally intelligent leaders:
- Maintain objectivity by recognizing how emotions influence judgment
- Balance analytical data with emotional insights from stakeholders
- Make difficult decisions while preserving relationships and trust
- Communicate challenging messages with both clarity and empathy
INNOVATION CATALYSTS
Leaders with high emotional intelligence create psychological safety that accelerates innovation by:
- Encouraging appropriate risk-taking without fear of punishment
- Reading subtle emotional cues that indicate untapped creative potential
- Managing the natural tensions that arise during collaborative innovation
- Fostering environments where constructive challenge is welcomed
EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE FOR EMPLOYEE DEVELOPMENT AND SUCCESSION PLANNING
Developing emotional intelligence throughout your organization creates a sustainable competitive advantage and builds your leadership pipeline:
ACCELERATED LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT
The EQ-i 2.0 provides a precise roadmap for developing future leaders by:
- Identifying specific emotional competencies that need strengthening
- Creating targeted development interventions with measurable outcomes
- Providing a framework for ongoing feedback and growth
- Establishing benchmarks for tracking leadership evolution
SUCCESSION PLANNING PRECISION
Emotional intelligence assessments reveal critical insights that technical evaluations miss:
- Leadership potential indicators beyond current performance metrics
- Adaptability markers that predict success during organizational change
- Relationship competencies essential for senior leadership effectiveness
- Stress resilience factors that determine long-term leadership sustainability
HIGH-POTENTIAL IDENTIFICATION
The EQ-i 2.0 helps identify emerging leaders who possess:
- The self-awareness to recognize their impact on others
- The relationship skills to influence across organizational boundaries
- The adaptability to thrive during transformation
- The decision-making capabilities to balance emotions with analysis?
Areas the EQ-i Model Measures
The EQ-i 2.0 uses a sophisticated 1-5-15 structure to assess emotional intelligence across five composite areas and fifteen specific subscales. This comprehensive approach provides unparalleled insight into the emotional and social functioning that drives leadership effectiveness:
1. SELF-PERCEPTION
How you understand and evaluate yourself
- Self-Regard: Respecting yourself while understanding your strengths and limitations. Leaders with healthy self-regard make decisions with confidence, acknowledge mistakes without self-criticism, and project authentic authority that inspires trust.
- Self-Actualization: Persistently pursuing meaningful objectives and engaging in activities that lead to personal growth and professional fulfillment. Leaders who score high in self-actualization continuously evolve their capabilities, embrace challenging assignments, and inspire similar growth in others.
- Emotional Self-Awareness: Recognizing and understanding your own emotions, their causes, and their impact on your thoughts, decisions, and interactions with others. Leaders with strong emotional self-awareness navigate high-pressure situations more effectively, recognize emotional triggers before they escalate, and make more objective decisions during organizational tension.
2. SELF-EXPRESSION
How you express yourself and your emotions
- Emotional Expression: Constructively expressing emotions with appropriate transparency. Leaders skilled in emotional expression communicate authentically, create psychological safety for their teams, and model appropriate vulnerability that builds trust.
- Assertiveness: Communicating feelings, beliefs, and thoughts openly while defending perspectives in a socially acceptable manner. Assertive leaders address difficult issues directly, navigate conflict productively, and advocate effectively for their teams and ideas.
- Independence: Making decisions autonomously while balancing input from others. Leaders with healthy independence take ownership of decisions, operate effectively without constant approval, and empower others to act with appropriate autonomy.
3. INTERPERSONAL
How you develop and maintain relationships
- Interpersonal Relationships: Building and sustaining mutually satisfying connections characterized by trust and compassion. Leaders who excel in interpersonal relationships build strong networks across organizational boundaries, foster psychological safety, and create high-performing teams with strong commitment.
- Empathy: Understanding and appreciating others' perspectives, even when they differ from your own. Empathetic leaders read subtle emotional cues, connect with diverse stakeholders, and navigate the human dynamics of organizational change with sensitivity.
- Social Responsibility: Contributing meaningfully to groups and the larger community. Leaders with strong social responsibility align organizational objectives with broader purpose, inspire discretionary effort from teams, and create cultures where people find meaning in their work.
4. DECISION-MAKING
How you use emotions in your thinking and decision processes
- Problem-Solving: Finding solutions to problems where emotions are involved. Leaders skilled in emotion-infused problem-solving navigate complex challenges with both analytical rigor and emotional intelligence, addressing both technical and human dimensions of issues.
- Reality Testing: Remaining objective by seeing situations as they truly are, not as you wish or fear them to be. Leaders with strong reality testing maintain accuracy in their perceptions, avoid confirmation bias, and make decisions based on objective assessment rather than emotional reactions.
- Impulse Control: Resisting or delaying impulses to act, particularly under stress. Leaders with developed impulse control respond thoughtfully rather than reactively during crises, maintain composure under pressure, and create psychological safety even during tense situations.
5. STRESS MANAGEMENT
How you cope with challenges and remain effective under pressure
- Flexibility: Adapting emotions, thoughts, and behaviors to unfamiliar, unpredictable, and dynamic circumstances. Flexible leaders navigate organizational change effectively, adjust strategies when circumstances shift, and remain open to diverse perspectives and approaches.
- Stress Tolerance: Coping with difficult situations and believing in your ability to influence outcomes positively. Leaders with high stress tolerance maintain effectiveness during organizational pressure, make clear decisions during ambiguity, and remain centered during turbulence.
- Optimism: Maintaining a positive outlook despite setbacks, focusing on what can be controlled. Optimistic leaders inspire confidence during challenging times, persevere through obstacles, and help others maintain motivation during extended transformation initiatives.
The versatility of the EQ-i 2.0 makes it an invaluable tool across multiple organizational applications:
LEADERSHIP DEVELOPMENT
Equip leaders at all levels to:
- Navigate the balance between challenging teams and maintaining engagement
- Make difficult decisions while preserving relationships
- Drive transformational change while managing the emotional dynamics of transition
- Create environments where strategic discomfort becomes productive rather than destructive
TEAM EFFECTIVENESS
Build high-performing teams that:
- Communicate effectively during periods of pressure and change
- Navigate conflict productively to reach better decisions
- Leverage diverse perspectives and work styles
- Maintain cohesion during organizational transformation
ORGANIZATIONAL TRANSFORMATION
Support successful change initiatives by:
- Developing change leaders with the emotional intelligence to navigate resistance
- Identifying emotional barriers to transformation early in the process
- Building resilience during extended periods of uncertainty
- Creating cultures where productive discomfort drives innovation
EXECUTIVE COACHING
Provide targeted development for senior leaders:
- Identify specific emotional intelligence competencies that impact leadership effectiveness
- Create precision development plans with measurable outcomes
- Build self-awareness that accelerates behavioral change
- Establish benchmarks for tracking leadership evolution
EQ-i 2.0 WORKPLACE REPORT
Designed for professionals at any career stage who want to understand how their emotional intelligence impacts their workplace effectiveness and interpersonal impact. This report provides::
- Detailed scores across all 15 subscales
- Analysis of impact on daily workplace functioning
- Specific strategies for leveraging strengths and addressing development areas
- Action planning tools for continuous improvement
EQ-i 2.0 LEADERSHIP REPORT
Designed specifically for leaders, comparing results against a benchmark of over 200 high-performing executives:
- Leadership-specific analysis of emotional intelligence impact
- Identification of potential derailment patterns
- Comparison to leadership best practices
- Targeted development strategies for maximizing leadership potential
With the EQ-i 2.0 reports, you can leverage your strengths and identify your weaknesses. By identifying weaknesses in different areas, you can immediately walk away with an action plan to begin improving the weak areas. Your levels of emotional intelligence can change over time and you can create development action plans to develop in targeted areas and help you fulfill your leadership potential
THE ADVANTEDGE APPROACH TO EMOTIONAL INTELLIGENCE
At AdvantEdge Leadership, we integrate the EQ-i 2.0 assessment into our proprietary Strategic Transformation methodology:
- Precision Diagnosis: We begin with the EQ-i 2.0 assessment to establish your emotional intelligence baseline
- Strategic Integration: We connect your EQ-i results to specific business challenges and opportunities
- Targeted Development: We design customized interventions that address your unique emotional intelligence profile
- Sustainable Implementation: We provide ongoing coaching to reinforce new behaviors and patterns
- Measurable Impact: We track progress through objective metrics and repeat assessments
BEGIN YOUR TRANSFORMATION JOURNEY
Developing emotionally intelligent leaders is the single most powerful leverage point for organizations seeking to drive innovation, improve efficiency, and navigate transformation successfully. Contact AdvantEdge Leadership today to schedule your EQ-i 2.0 assessment and discover how enhanced emotional intelligence can transform your leadership capacity and organizational performance.


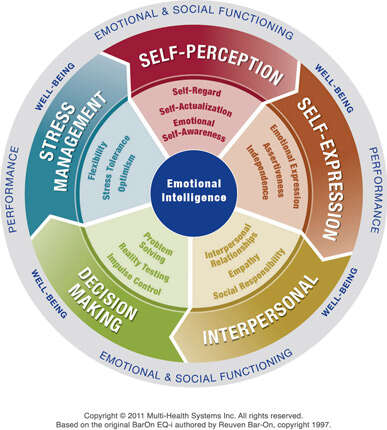 widely used Emotional Intelligence instruments in the world.
widely used Emotional Intelligence instruments in the world.